How Does a Drip System Work? From Water Source to Plant Roots
Introduction
In an era of increasing water scarcity and climate uncertainty, drip irrigation has emerged as one of the most efficient ways to deliver water to crops. Unlike traditional flood or sprinkler irrigation, which can waste significant amounts of water, drip systems deliver water directly to plant roots with minimal loss.
But how exactly does a drip irrigation system function? In this article, we’ll break down the journey of water—from its source to the plant roots—and explain the science behind precision farming and water efficiency.
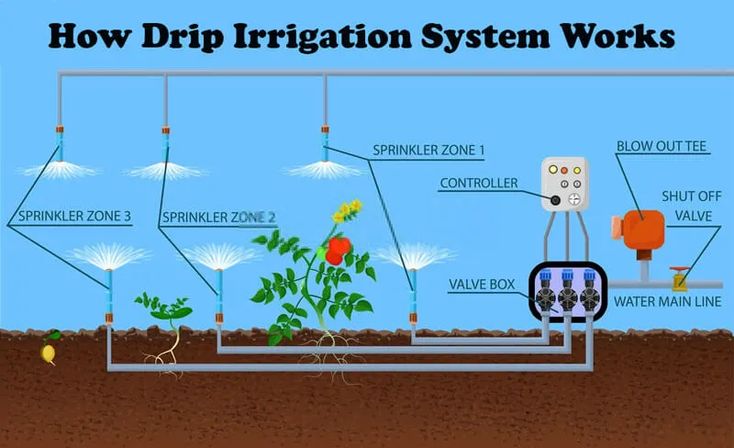
The Components of a Drip Irrigation System
A drip irrigation system consists of several key components that work together to ensure controlled and efficient water delivery:
1. Water Source
- Wells, reservoirs, or municipal supplies provide the initial water.
- The system can also use rainwater harvesting or treated wastewater for sustainability.
2. Pump & Pressure Regulator
- A pump ensures water flows through the system (unless gravity-fed).
- A pressure regulator maintains consistent water pressure (typically 10-30 PSI) to prevent leaks or bursts.
3. Filtration System
- Sand filters, screen filters, or disc filters remove debris, algae, and sediment that could clog emitters.
- Clean water is crucial for long-term system efficiency.
4. Mainline & Submain Pipes
- Mainlines (usually PVC or polyethylene) carry water from the source to the field.
- Submains distribute water to individual drip lines or tapes.
5. Drip Lines & Emitters
- Drip lines (flexible tubes with built-in emitters) or separate drippers release water drop by drop.
- Emitters control flow rates (typically 0.5 to 4 gallons per hour).
6. Valves & Controllers
- Manual or automated valves control water flow to different zones.
- Smart controllers adjust watering based on weather, soil moisture, or timers.
How Water Moves Through a Drip System
Step 1: Water Extraction & Pressurization
- Water is drawn from a well, reservoir, or municipal line.
- A pump (or gravity, in some cases) pressurizes the system.
Step 2: Filtration & Pressure Regulation
- Water passes through filters to remove impurities.
- A pressure regulator ensures optimal flow without damaging pipes.
Step 3: Distribution Through Pipes
- Water travels through mainlines and submains to reach different crop zones.
- Valves allow farmers to control which sections receive water.
Step 4: Precise Water Delivery via Emitters
- Water drips slowly from emitters directly into the root zone.
- This minimizes evaporation, runoff, and weed growth.
Step 5: Absorption by Plant Roots
- The slow release allows water to infiltrate deeply, encouraging strong root development.
- Fertilizers (fertigation) can be injected into the system for nutrient efficiency.
Why Drip Irrigation Is More Efficient Than Other Methods

Key Advantages:
✔ Saves 30-60% more water than traditional methods.
✔ Reduces fertilizer waste through fertigation.
✔ Works on slopes & uneven terrain where flood irrigation fails.
✔ Lowers labor costs with automation.
Applications of Drip Irrigation
1. Large-Scale Farming
- Used for fruits (grapes, citrus), vegetables (tomatoes, lettuce), and field crops (cotton, sugarcane).
2. Greenhouses & Nurseries
- Ensures consistent moisture for delicate seedlings and high-value plants.
3. Vineyards & Orchards
- Improves fruit quality and yield by preventing over/under-watering.
4. Home Gardens & Landscaping
- Ideal for drought-prone areas and water-conscious homeowners.
Challenges & Maintenance Tips
Potential Issues:
❌ Clogging – Sediment, algae, or minerals can block emitters.
❌ Rodent Damage – Animals may chew through drip lines.
❌ High Initial Cost – Requires investment in tubing, filters, and controllers.
Maintenance Best Practices:
✔ Flush the system regularly to prevent clogs.
✔ Check filters and clean/replace them as needed.
✔ Inspect for leaks and repair damaged tubing.
✔ Monitor soil moisture to avoid overwatering.
The Future: Smart Drip Irrigation & IoT
Emerging technologies are making drip systems even smarter:
- Soil moisture sensors adjust watering in real time.
- AI-powered controllers optimize schedules based on weather forecasts.
- Solar-powered pumps reduce energy dependence.
As precision farming evolves, drip irrigation will remain a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture.
Conclusion
A drip irrigation system is a highly efficient, scientifically designed method of delivering water exactly where plants need it—directly to their roots. By minimizing waste and maximizing crop health, drip systems play a vital role in modern agriculture, especially in water-scarce regions.
Whether you’re a farmer, gardener, or sustainability advocate, understanding how drip irrigation works can help you conserve water, save money, and grow healthier plants.
